
Mold-Masters Co-injected Pill Bottle
CO-INJECTED MULTI-LAYER PILL BOTTLE
Medical Packaging Manufacturer Selects Mold-Masters Technology for Production Enhancements
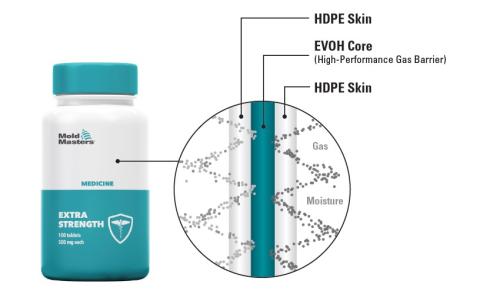
A large medical packaging manufacturer recently adopted Mold-Masters Co-Injection Technology for its pill bottle co-injection application, yielding performance improvements. The manufacturer now has the ability to inject their proprietary material blend to improve container performance (extending shelf life of products), to enhance part quality (appearance and strength), significantly minimize scrap, and eliminate secondary operations.
Mold-Masters co-injection technology utilizes a proprietary nozzle design that combines two different resins into a single 3-layer melt stream. By incorporating a high-performance barrier as the core layer in packaging products, co-injection extends shelf life, maintaining freshness and flavor, longer than mono-layer blends and other conventional alternatives. From a processing perspective, co-injection increases productivity by eliminating the requirement for secondary processes and minimizes scrap. Mold-Masters co-injection technology is fully customizable to create a moisture, gas, or light barrier for containers of all shapes and sizes without any penalty to a molder’s existing cycle time.
In this specific pill bottle co-injection application, the customer used a combination of materials. HDPE was used for the inner and outer skin layers, while EVOH, a high-performance gas barrier, was used for the core layer. By leveraging the barrier characteristics of these two materials, it offers enhanced protection for medical formulations and has allowed them to extend the shelf life of medical pills inside the containers that are sensitive to oxygen and moisture permeation to avoid spoilage. These new premium medical containers offer the potential to eliminate conventional moisture packets that are traditionally included to protect medicine. This can eliminate the secondary operation costs of including them in the packaging.

Co-injected (IBM) bottles also offer sustainability benefits over Extrusion Blow Molded (EBM) bottles. Co-injected bottles significantly minimize production scrap, allow for lighter weight bottles and provide enhanced bottle quality. The EBM manufacturing process, on the other hand, is a high-scrap operation due to the secondary operations (flash removal) required for each bottle. The smaller the bottle, the higher percentage of scrap (up to 50% scrap). Normally this scrap can be reground and reused to make more monolayer bottles. However, when barrier layers are introduced, these barriers represent contamination, which make it unsuitable for regrinding and reprocessing.
Compared to EBM, the IBM process offers greater potential for such packaging products to be recycled (depending on regional recycling programs). IBM does not incorporate additional adhesive layers to keep the different layers together, which are present in EBM produced products. This allows IBM bottle material layers to be more easily separated as part of a recycling process.
Additionally, the co-injection process eliminates bottle quality limitations that are present with the EBM process. These include the potential for the barrier to be exposed in EBM bottles that can create issues for heat sealing, difficultly holding neck tolerances, uneven barrier thicknesses, visible die lines/extrusion lines and pinched bottoms, which can be unstable and increase risks associated with stress cracking (bottle failure).
